Posted By Akio
Posted By Akio- Comments 0
What is Eye Dilation?
Eye dilation, also known as mydriasis, refers to the widening of the black circle in the centre of your eye, known as the pupil. The pupil lets light enter your eyes, and the amount of light is controlled by the iris, which is the coloured part of the eye. In the bright light, the muscles contract, making the pupil smaller to prevent excessive light from entering. Conversely, in dim light, the muscles relax, causing the pupil to dilate and allow more light in. Dilated eyes can occur due to natural reasons such as changes in brightness, but if the pupil does not change in size, it could mean that it’s not functioning properly.
This blog dives deep into the phenomena of dilated eyes, the significance of eye drops during eye tests, and what to expect while getting dilated eyes.
Why Do Eye Doctors Dilate Your Eyes
Eye dilation plays a crucial role in comprehensive eye examinations. Here’s why your doctor might use eye dilation drops:
- Enhanced view of the eye: Dilated eyes make it convenient for the doctor to examine the interior of your eye. This allows them to see the retina, and the optic nerve, and effectively prevent eye conditions that could lead to vision loss.
- Detection of eye diseases: Dilation helps diagnose various eye conditions, including:
- Glaucoma: This condition involves increased pressure within the eye that can damage the optic nerve and lead to vision loss. By examining the optic nerve during dilation, the doctor can assess potential glaucoma risks.
- Diabetic retinopathy: This complication of diabetes damages blood vessels in the retina. Dilation allows for early detection of these changes.
- Age-related macular degeneration (AMD): This is a leading cause of vision loss in older adults. Dilation helps identify early signs of AMD, which can be crucial for managing the condition.
- Macular hole: This is a small opening in the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp central vision. Dilation aids in diagnosing macular holes.
Also Read: Essential Vitamins and Nutrients for Optimal Eye Health | Akio
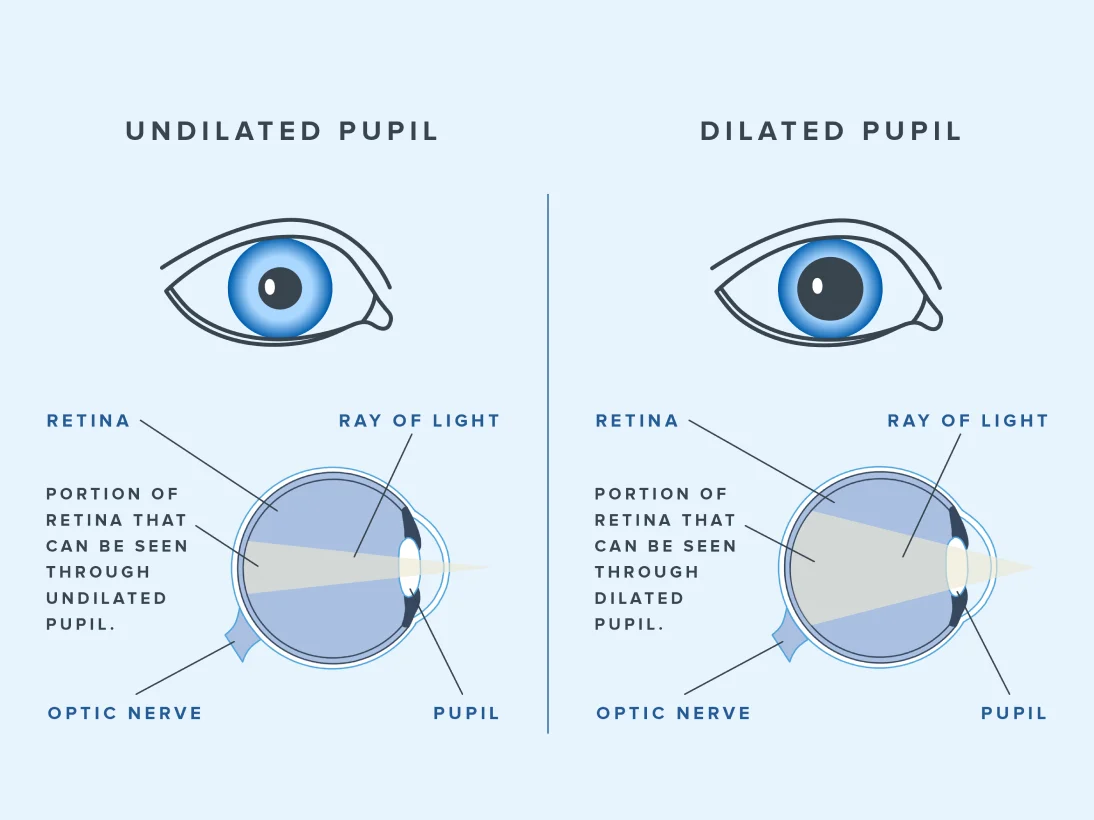
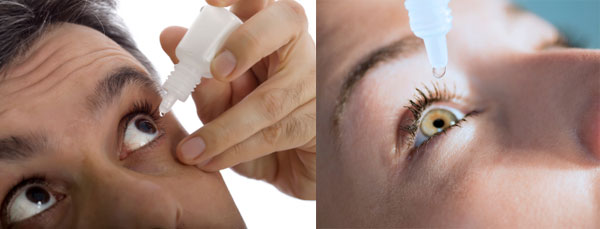
What to Expect During an Eye Dilation Test
The procedure for dilated eyes is generally quick and painless. It involves the following steps:
- Visual Acuity Test to identify your vision by reading both distant and close letters.
- Visual Field Test to check your peripheral vision without any eye movement.
- Eye Muscle Function test to evaluate any defect in your eye movements while following a moving object.
- Pupil Response Test to check how your pupils respond to the light by shining a flashlight in your eyes.
- Tonometry Test which is done by blowing a puff of air into your eyes to check the eye pressure
- Dilation by using eye drops for dilated eyes that helps in widening the pupil.
The Role of Eye Dilation Drops in the Procedure
During the eye test, it’s typical for the doctor to apply eye dilation drops to your eyes. These drops contain medications that cause the muscles in the iris to relax, leading to the widening of the pupil. Although they are typically safe, it’s important to inform your doctor about any allergies or medications you are taking, as some medications can interact with dilation drops.
How Long Does Eye Dilation Last
Generally, the effects of eye dilation wear off within 4-6 hours. However, it can take up to 24 hours for your vision to return to normal, especially if strong dilation drops are used.
The duration of the effects of dilated eyes can vary depending on several factors, including:
- Dose: Children typically require higher doses of eye dilation drops, which makes the effects last longer.
- Eye colour: Those with light-coloured eyes may feel longer effects of dilating drops.
- Age: Younger individuals tend to experience longer dilation effects compared to older adults.
What Not to Do After Eye Dilation?
While the effects of eye dilation drops are temporary, they may cause discomfort and restrict some of your activities due to making your eyes blurry and sensitive to light.
Here are some precautions to take after eye dilation:
- Avoid driving as it can get difficult to focus on nearby objects or see clearly in dim light.
- Avoid rubbing your eyes as it can cause irritation or damage.
- Avoid bright light by wearing sunglasses or a hat.
- Avoid activities that require you to focus, such as reading, using smartphones, knitting, etc.
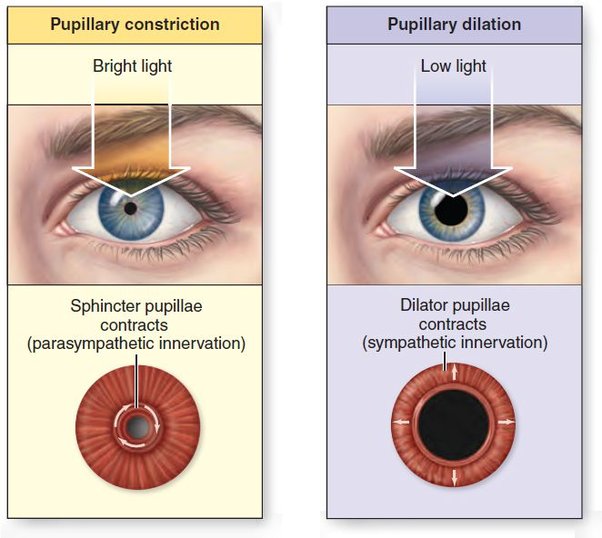
Common Reasons for Variations in Eye Pupil Dilation
While eye dilation is a natural response to light, some instances can cause variations in the dilated eyes, such as:
- Medical conditions like brain injury, tumour, migraine, etc.
- Certain medications with side effects like antidepressants, antihistamines, etc.
- Recreational drugs such as cocaine, LSD, ecstasy, etc.
It is crucial to note that while occasional variations in pupil dilation are not necessarily a cause for concern, persistent variations, sudden changes in pupil size, and dilation accompanied by symptoms like vision loss, severe headache, or eye pain, make it important to seek medical attention.
Conclusion
Understanding dilated eyes empowers you to indulge in active eye care. While eye dilation is a standard procedure during eye tests, it helps to know its purpose, what to expect, and potential variations to alleviate any anxieties that may occur. If you have any concerns about eye dilation or experience unusual pupil dilation, it is important to discuss them with your eye doctor for early detection and diagnosis to maintain optimal eye health and vision throughout your life.
Visit AKIO, the trusted Retina Treatment in Delhi NCR, for advanced treatments and personalized care. Book your appointment today!