
-
 Posted By Akio
Posted By Akio -
-
Comments 0
Considering modern human health, diabetes has become a common health condition, and it is astoundingly increasing day by day. Among the various consequences of diabetes, diabetic retinopathy is the one that will affect your retina. There are a few types of diabetes that people usually suffer from, and all such individuals with any of its types can be sufferers of diabetic retinopathy.
As renowned as one of the best ophthalmologists in Delhi, AK Institute of Ophthalmology we are committed to our patients’ optimum health. We believe that early medical intervention is highly crucial to finding a cure without many consequences. In this article, we explore and create awareness about diabetic retinopathy, its intricacies, early signs, latest treatment advancements, and how to prevent it.
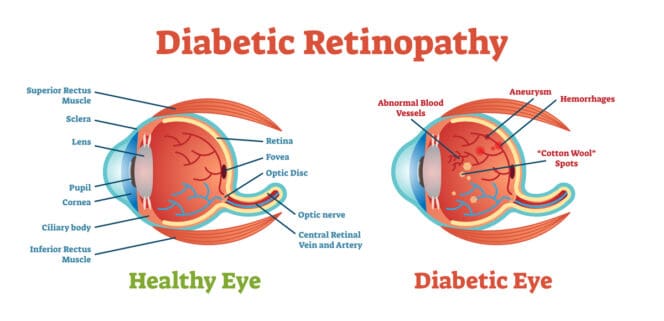
What Is Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a diabetes-related eye condition that affects the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye.
High blood sugar levels can cause these vessels to swell, leak, or become blocked, leading to vision problems.
There are two main stages: non-proliferative, where early changes occur, and proliferative, which involves new blood vessel growth that can cause severe vision loss.
Causes
Diabetic retinopathy primarily results from prolonged high blood sugar levels associated with diabetes. The key causes include:
- Chronic Hyperglycemia: Elevated blood glucose damages blood vessels in the retina over time, leading to leakage and abnormal growth.
Poor Diabetes Management: Inconsistent and uncontrolled blood sugar control and neglecting regular eye check-ups increase the likelihood of developing the condition.
High Blood Pressure: Hypertension can worsen blood vessel damage and increase the risk of retinopathy.
High Cholesterol Levels: Elevated cholesterol can contribute to the narrowing and hardening of blood vessels, exacerbating retinopathy.
Duration of Diabetes: The longer a person has diabetes, the greater the risk of developing retinopathy.
Other Factors: Genetics, smoking, and pregnancy can also influence the risk of diabetic retinopathy.
Symptoms
Symptoms of diabetic retinopathy can vary depending on the stage of the disease but often include:
- Blurred Vision: This may come and go, affecting one or both eyes.
- Dark or Empty Areas in Vision: You may notice spots or gaps in your visual field.
- Difficulty Seeing at Night: Low-light conditions can become particularly challenging.
- Fluctuating Vision: Sudden changes in vision clarity may occur.
- Colour Distortion: Colours may appear faded or altered.
- Floaters: Small spots or lines that drift across your field of vision.
Also Read:- How to Use Contact Lenses Safely
Diabetic Retinopathy Prevention
- Regular Eye Exams: Schedule comprehensive dilated eye exams at least once in 6 months to detect any changes early.
- Blood Sugar Control: Maintain optimal blood sugar levels through a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and medication adherence. Get regular sugar check-ups with your doctors, along with every 3 months HbA1C to be measured and monitored.
- Blood Pressure Management: Keep blood pressure within recommended limits to reduce strain on blood vessels.
- Cholesterol Management: Monitor and manage cholesterol levels to lower the risk of cardiovascular issues that can affect eye health.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Avoid smoking, eat a nutritious diet rich in fruits and vegetables, and engage in regular exercise to improve overall health.
- Education: Stay informed about diabetes and its complications to make informed health decisions.
Diagnosis and treatment:
AK Institute of Ophthalmology provides the latest, most precise and state-of-the-art technology for diagnosis and testing of our retina, cataract and glaucoma, in order to check the impact of diabetes on your eye.
- Eye Dilation exam: Diabetic Macular Edema is diagnosed through an eye dilation exam in which eye drops are inserted to expand your pupils to allow a better look within.
- Fluorescein Angiography: Then, a dye is injected through your arm, which travels through your eye’s blood vessels and produces images.
- Optical Coherence Tomography: Finally, the OCT test is taken to monitor the thickness of your retina and any fluid leakage.
Complications
Complications of diabetic retinopathy can lead to serious vision problems and include:
- Vision Loss: As the condition progresses, patients may experience blurred vision, dark spots, or complete vision loss.
- Macular Edema: Swelling in the macula, the central part of the retina can occur due to leaking blood vessels, leading to distorted or blurred central vision. Such a condition usually requires some intervention.
- Bleeding in retina: Uncontrolled diabetes leads to the blood vessels leaking and causing bleeding in the retina. This leads to blurred vision and requires intervention.
- Retinal Detachment: The growth of abnormal blood vessels can pull the retina away from its supporting tissue, resulting in a detached retina, which may require immediate surgical intervention.
- Glaucoma: Increased pressure within the eye may occur due to new blood vessel formation, increasing the risk of glaucoma, which can damage the optic nerve and result in vision loss.
- Cataracts: People with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing cataracts, which can lead to cloudy vision and may require surgical removal.
- Blindness: In severe cases, untreated diabetic retinopathy can lead to irreversible blindness.
Why AKIO for Retina damage due to Diabetes:
AK Institute of Ophthalmology offers treatments like:
1. Laser Treatment (Photocoagulation)
- This laser treatment is used to seal or destroy leaking blood vessels in the retina, reducing swelling in the macula.
- Laser treatment that targets areas of the retina away from the macula to shrink abnormal blood vessels and prevent further bleeding.
2. Anti-VEGF Injections
Anti-VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) injections are used to block the growth of abnormal blood vessels. These injections can reduce swelling, prevent blood vessel leakage, and help restore vision.
These injections are administered into the eye and may require multiple treatments over time.
3. Steroid Injections
Corticosteroid injections or implants can be used to reduce inflammation and swelling in the retina. These implants release medication slowly over several months to help manage retinal swelling.
4. Vitrectomy
A Vitrectomy is a surgical procedure where the vitreous gel (the clear, jelly-like substance in the middle of the eye) is removed. This is usually done if there is significant bleeding (vitreous hemorrhage) or scar tissue pulling on the retina (tractional retinal detachment) or in any other conditions. The vitreous is replaced with a clear solution to maintain the shape of the eye and relieve pressure.
5. Blood Sugar and Blood Pressure Control
Managing diabetes effectively with tight blood sugar control (HbA1c levels ideally not above 7%) can slow the progression of diabetic retinopathy. Additionally, controlling high blood pressure and cholesterol levels can reduce the risk of further damage to the retinal blood vessels.
6. Lifestyle Changes and Monitoring
- Regular eye exams: Annual eye exams are essential for early detection and timely treatment of diabetic retinopathy.
- Healthy diet: Maintaining a diabetes-friendly diet that is low in sugar and carbohydrates can help prevent spikes in blood sugar levels.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity helps improve blood sugar control and overall vascular health.
Conclusion
Diabetic retinopathy is a leading cause of vision impairment and blindness among adults, particularly in those with diabetes. As AKIO is dedicated to preserving and enhancing vision, we understand the profound impact this condition can have on individuals and their quality of life.
If you are diabetic and you think that your symptoms match the ones mentioned above, we request that you not delay before seeing an eye specialist.
At AKIO, we are devoted to our patients and with the advanced treatment options, we are successful as a doctor and guide to many such patients with vision conditions.
Early diabetic retinopathy often has no noticeable symptoms. When symptoms appear, they may include blurred or fluctuating vision, floaters (spots or lines), dark or empty areas in vision, and difficulty with detailed tasks. Eye pain or pressure can occur in advanced stages.
Prevent diabetic retinopathy by controlling blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol. Maintain a healthy diet, exercise regularly, avoid smoking, and attend annual dilated eye exams. Early detection and management of diabetes are key to protecting your vision and reducing the risk of complications.
Current treatments include laser therapy, anti-VEGF injections to reduce abnormal blood vessel growth, and vitrectomy for advanced cases with bleeding. Ongoing research explores new medications and surgical techniques to improve outcomes and slow disease progression.
High blood sugar damages the tiny blood vessels in the retina, causing them to swell, leak, or close. This leads to oxygen deprivation, abnormal vessel growth, and fluid buildup, resulting in vision changes and, if untreated, significant vision loss.
Early treatment can slow or stop the progression of diabetic retinopathy and prevent severe vision loss, but it usually cannot fully reverse existing damage. Early detection and management are crucial for preserving vision and preventing further deterioration.
Adopt a balanced diet rich in whole grains, vegetables, and lean proteins. Exercise regularly, control blood sugar and blood pressure, avoid smoking, and maintain a healthy weight. Regular eye check-ups and following your doctor’s advice are essential for reducing risk.
Diabetic patients should have a comprehensive dilated eye exam at least once a year, even if they have no symptoms. Those with risk factors or existing eye changes may need more frequent screenings as advised by their eye specialist.
Recent Posts
- How Mr Verma’s Sudden Vision Loss Was Reversed Through Emergency Retinal Detachment Surgery (Case Study)
- Retinal Risks After Eye Trauma: Why Even Minor Injuries Matter
- Top 10 Most Asked Retina Questions Answered by our Retina Surgeon
- How Mr Sharma Regained Vision After Sudden Retinal Detachment — Within 24 Hours of Surgery at AKIO (Case study)
- Are Retina Injections Painful? Read a patient’s experience!



